In our increasingly hyperconnected world, where digital interactions underpin nearly every facet of our lives, the importance of cyber hygiene has never been more pronounced. Just as personal hygiene practices are crucial for maintaining good health and preventing disease, cyber hygiene practices are fundamental to securing our digital health and protecting against cyber threats. This article explores the concept of cyber hygiene, outlines best practices for individuals and organizations, and presents real-world examples to illustrate the practical application of these practices.

Understanding Cyber Hygiene
Cyber hygiene refers to the routine practices and precautions that individuals and organizations undertake to maintain the health and security of their digital environments. It encompasses a wide range of activities, from securing personal devices and data to implementing comprehensive cybersecurity policies within organizations.
Why Is Cyber Hygiene Important?
The digital landscape is rife with threats, from malware and phishing attacks to data breaches and identity theft. Poor cyber hygiene can lead to compromised personal information, financial loss, and even damage to an organization’s reputation. By adopting good cyber hygiene practices, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability to cyber threats.
Best Practices for Individuals
1. Use Strong, Unique Passwords
One of the simplest yet most effective cyber hygiene practices is the use of strong, unique passwords for all online accounts. A strong password should be a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols, and it should be changed regularly. Consider using a password manager to securely store and manage passwords.
This is the classic recommendation of every cyber security analyst and network admin ever and to a regular person they may not understand why this is important. The answer is brute-forcing. The act of brute-forcing is a hackers last resort(most of the time), its system and time intensive and in my experience almost never works.
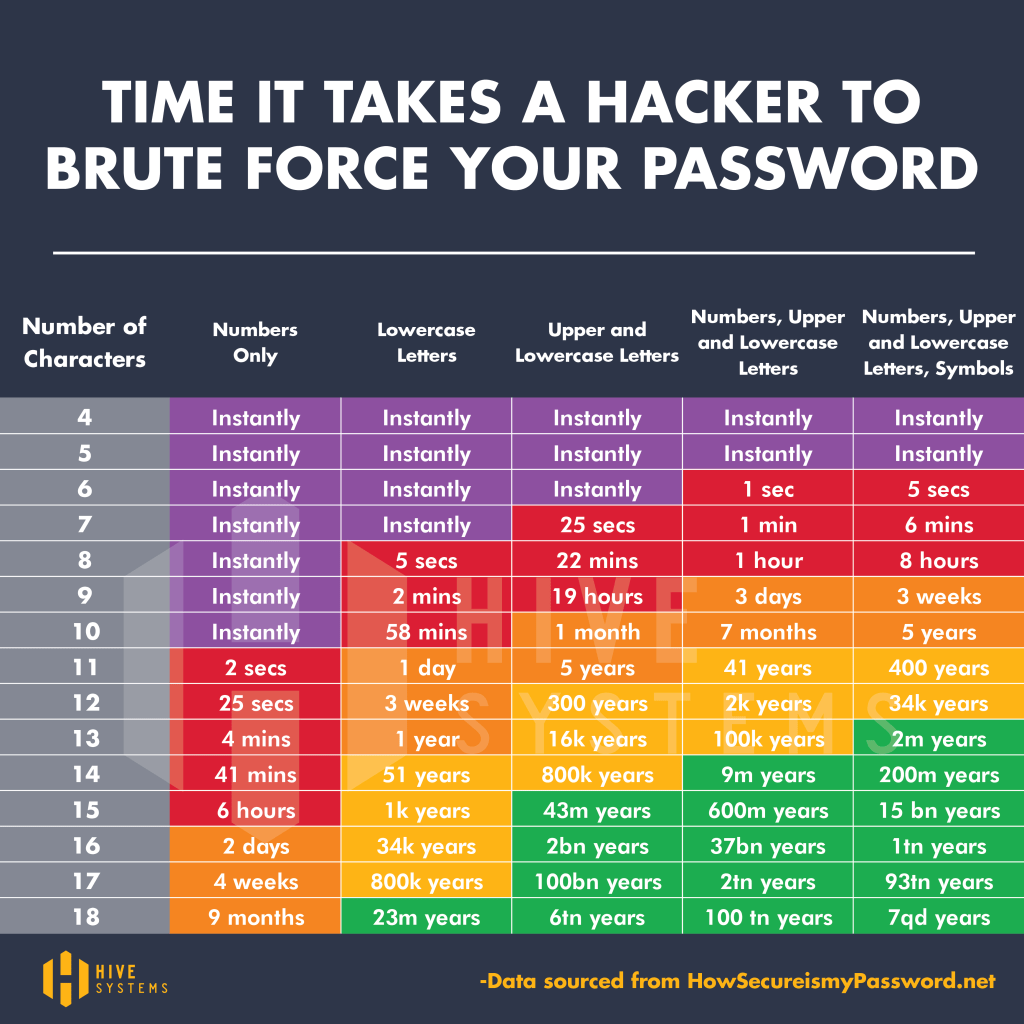
Brute-forcing is the act or trying every combination of characters to try and guess a password. There are many ways a system can nullify these attacks but a strong password is usually the easiest. A password of 12345678 will take an average computer seconds to brute-force but a 12 character password with capital letters, numbers and special characters can take thousands of years for even powerful machines to break.
Below is a table of how long your average computer would take to brute-force passwords taken from HowSecureIsMyPassword.net.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification in addition to your password. This could be a text message code, an email, or a notification on a trusted device.
2FA is a standard now-a-days and it adds a large amount of security to your accounts. It can be bypassed however it depends on known vulnerabilities or phishing attacks to beat so its one of the easiest and best ways to add security to your life online and with apps like Microsoft’s authenticator its become alot easier to implement.
3. Regularly Update Software and Devices
Software developers regularly release updates to patch security vulnerabilities. Ensuring that your operating system, applications, and devices are up-to-date is a crucial aspect of maintaining cyber hygiene.
This is an obvious one but never the less important. Every day bug hunters are finding new vulnerabilities in apps, programs and even operating systems, remember the recent Apache vulnerability dubbed log4j that caused havoc on the internet. Updates are what patches these vulnerabilities out of the program and protects you and your devices.
4. Be Wary of Phishing Attempts
Phishing is a common technique used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into revealing personal information. Be cautious about opening emails or clicking on links from unknown sources, and verify the authenticity of requests for personal information.
An oldie but a goodie. Phishing attacks are still the most common type of attack on the internet and will be for the foreseeable future. The thing about the attacks is that they can bypass alot of the security that programmers implement in their programs, clicking on a malicious link or downloading a file with malware can wreak havoc on a system.
Always check the authenticity of an email before opening it, not all phishing attacks are the bot driven crap that is sent to your junk mail 20 times a day, some can actually be very sophisticated and hidden very well.
Best Practices for Organizations
1. Conduct Regular Security Assessments
Organizations should conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities within their digital infrastructure. This can include penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security audits.
Pen-testing is something that needs to be more common place even for small to medium size businesses as they are the prime targets for most hackers.
2. Implement a Comprehensive Cybersecurity Policy
A comprehensive cybersecurity policy outlines the procedures and practices that employees must follow to protect organizational data. It should cover aspects such as password management, device usage, data encryption, and incident response protocols.
Businesses should always be following a strong ITIL processes and cyber security training should be constantly reinforced into every facet of a business not just the IT sections. HR, customer services, finance etc should be well aware of their role in the security of a system and business.
3. Provide Cybersecurity Training
Employees are often the weakest link in an organization’s cybersecurity defence. Providing regular cybersecurity training can equip employees with the knowledge to recognize and respond to cyber threats effectively.

4. Utilize Advanced Security Solutions
Organizations should invest in advanced security solutions such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. These tools can provide real-time protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
Real-World Examples
The Equifax Data Breach
In 2017, Equifax, one of the largest credit reporting agencies, suffered a massive data breach that exposed the personal information of 147 million people. The breach was attributed to the company’s failure to patch a known vulnerability in a web application framework it used. This example underscores the importance of regular software updates as a critical aspect of cyber hygiene.
The Twitter Bitcoin Scam
In July 2020, a major security breach of Twitter’s systems led to the compromise of several high-profile accounts, including those of Elon Musk, Barack Obama, and Joe Biden. The attackers used these accounts to promote a Bitcoin scam. This incident highlights the need for robust access control measures, including two-factor authentication, to protect against unauthorized access to sensitive accounts.
Conclusion
Cyber hygiene is not a one-time task but a continuous process that requires diligence and commitment. By adopting the best practices outlined in this article, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance their digital health and resilience against cyber threats. As the digital landscape evolves, so too will the nature of cyber threats, making the commitment to good cyber hygiene an ongoing necessity in our increasingly digital world.




Leave a comment