In the realm of cyber threats, phishing attacks stand out for their deceptively simple approach and devastatingly effective results. By impersonating legitimate entities and crafting compelling messages, cybercriminals manipulate users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malicious software. Understanding how to identify and mitigate phishing attacks has never been more important. In this guide, we’ll highlight examples and provide practical steps to safeguard against these threats.
Spotting Phishing Attacks: Know the Signs
- Mismatched Email Domains: Check the sender’s email address, not just their display name. For example, an email from a fraudster pretending to be Amazon might look like ‘service@amaz0n.com‘ instead of ‘service@amazon.com‘.
- Unsolicited Attachments or Links: Unexpected attachments or hyperlinks often hide malware. If an email from a seemingly trustworthy source prompts you to download a file or click a link, be skeptical.
- Sense of Urgency: Phishing emails often create a sense of urgency to provoke immediate action. Be wary of messages demanding immediate action to ‘verify your account’ or ‘update your payment details’.
- Request for Personal Information: Legitimate organizations typically do not ask for sensitive data through emails. Any message requesting usernames, passwords, bank details, or other private data should raise a red flag.
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: While not always the case, phishing emails often contain typos or awkward phrasing. Major organizations usually proofread their messages meticulously.
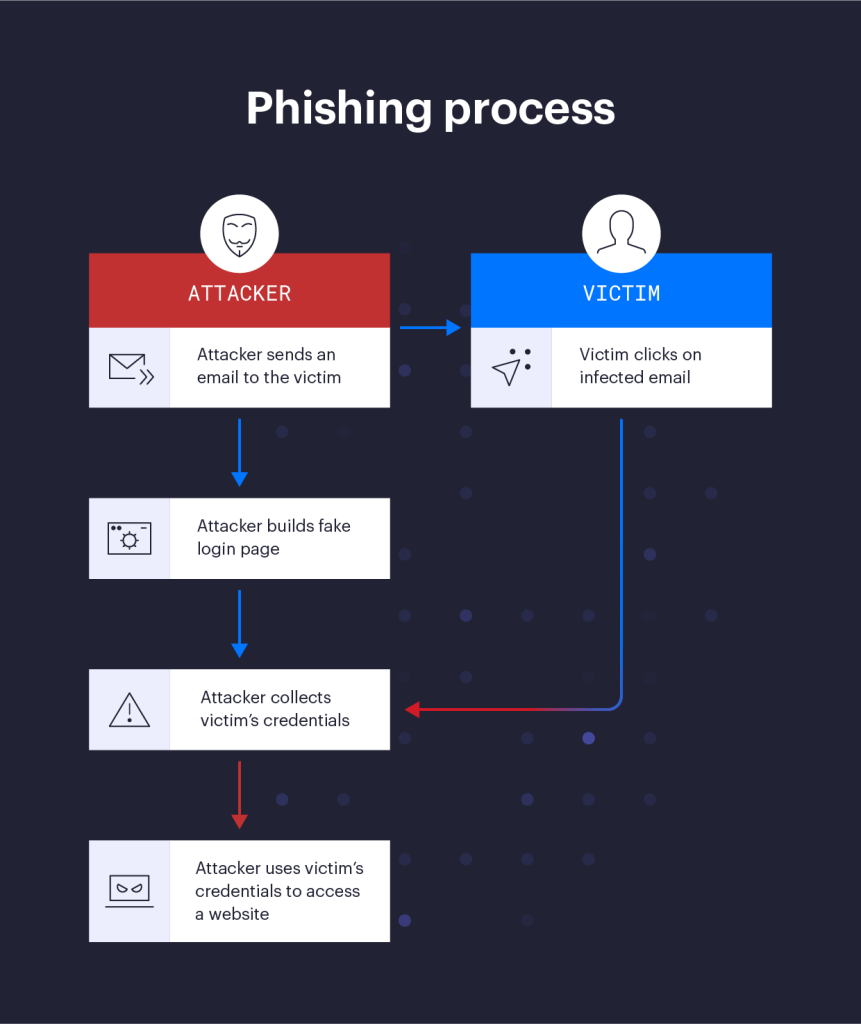
Preventing Phishing Attacks: Best Practices
- Stay Informed: Understanding the latest phishing techniques can help you identify attacks. Regularly check cybersecurity news or subscribe to cybersecurity threat alerts.
- Verify Before You Click: If an email urges you to visit a website, manually enter the website’s address into your browser rather than clicking the link provided in the email.
- Use Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Implementing 2FA adds an extra layer of security. Even if a phisher obtains your login credentials, they won’t be able to access your account without the second verification step.
- Install Antivirus Software: Reliable antivirus software can protect your devices by detecting and blocking phishing attempts and other threats.
- Educate Your Network: If you’re a business, educate your employees about phishing attacks. Simulated phishing exercises can be a practical tool for testing and improving your team’s readiness against phishing attacks.
Phishing attacks account for most of the data breaches you read in the news almost every day. Threat actors are getting better at crafting authentic looking emails with links and when targeted at individuals with a spear phishing attacks they can bypass much of a companies or individuals security measures.

Here are some of the most high profile phishing attacks that lead to data breaches in the past decade:
- Google and Facebook Phishing Scam (2017-2018): In one of the most high-profile cases, a Lithuanian man, Evaldas Rimasauskas, tricked Google and Facebook into wiring over $100 million into bank accounts he controlled. He had sent phishing emails that posed as a well-known Asian hardware vendor, which both companies did business with, leading to one of the most substantial losses due to phishing.
- Ubiquiti Networks Phishing Attack (2015): The American network technology company, Ubiquiti Networks, fell victim to a phishing attack that cost the company nearly $47 million. Fraudsters impersonated communications from the company’s finance department and instigated unauthorized international wire transfers.
- Anthem Phishing Attack (2015): Anthem, the second-largest health insurer in the United States, suffered a significant breach when hackers used a phishing email to gain access to a system administrator’s account. This attack led to the exposure of personal data of nearly 78.8 million insurers, including their names, birth dates, and Social Security numbers.
- Crelan Bank Phishing Attack (2016): Belgian bank Crelan lost around €70 million ($75.8 million) due to a sophisticated phishing attack. Fraudsters used phishing emails to steal staff login credentials, then made several transactions without detection.
- Milwaukee Bucks Phishing Attack (2016): A hacker impersonating the president of the NBA team Milwaukee Bucks sent an email to the team’s payroll department requesting W-2 tax forms for all players and staff. The information was sent, exposing the private data of many individuals associated with the team.
Each of these examples highlights the potential severity of phishing attacks, even against large, sophisticated organizations. It underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures, comprehensive employee training, and constant vigilance.
In the ever-evolving cyber landscape, phishing remains a persistent threat. By learning to spot the tell tale signs of phishing attacks and implementing preventative measures, we can significantly reduce our vulnerability to this common cyber threat. Remember, when it comes to phishing, vigilance is your strongest defence.




Leave a comment